Blog
Regents Earth Science: Understanding Moon Phases with a Helpful Worksheet
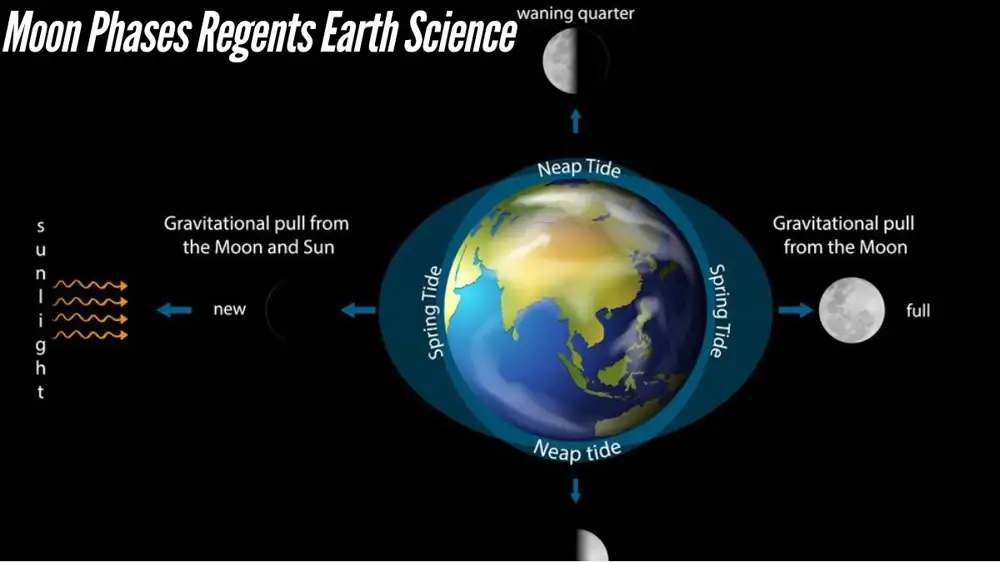
A key component of the Regents Earth Science curriculum is the study of Earth’s past, particularly in relation to astronomical phenomena like the phases of the Moon. The Moon phases hold a special place among the most interesting and visually captivating topics taught in the course. Understanding the phases of the Moon is essential for grasping its relationship with Earth and its position in the cosmos.
The Regents Earth Science Moon Phases Worksheet is a valuable resource for preparing for the Regents Earth Science exam. It helps students learn about the phases of the Moon, the causes behind them, and their impact on Earth. This article will break down the Moon phases, explain the worksheet structure, and offer tips to help you succeed on your exam.
Understanding the Moon Phases
A thorough comprehension of the Moon phases itself is essential before beginning the worksheet. The Moon’s various appearances during its orbit around the Earth are referred to as its phases. As the Moon travels through its orbit around the Earth, the angle between the Sun, Earth, and Moon changes, causing these phases.
The Moon’s roughly 29.5-day lunar cycle is divided into eight main phases that we can see. These stages are:
- New Moon: This phase occurs when the Moon is positioned between the Earth and the Sun, making it almost invisible from Earth. The Sun’s light is shining directly on the far side of the Moon.
-
Waxing Crescent:
A tiny portion of the Moon is visible after the New Moon. This phase is called waxing crescent because the visible part of the Moon is growing or “waxing.”
- First Quarter: In this phase, half of the Moon’s surface is visible. The right half of the Moon is lit up, and it’s known as the First Quarter because the Moon is about a quarter of the way through its cycle.
- Waxing Gibbous: The moon’s brightness keeps increasing. Between the First Quarter and the Full Moon is this period.
- Full Moon: The Sun’s light fills the Moon’s whole face with illumination. When the Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon, this phase takes place.
- Waning Gibbous: After the Full Moon, the light starts to decrease, and the Moon is now in the waning phase, or shrinking phase.
- Last Quarter: The left half of the Moon is visible during this phase. It is also called the Third Quarter, and it marks the final quarter of the lunar cycle.
- Waning Crescent: This is the final phase before the cycle starts again with the New Moon. The Moon’s luminous area keeps getting smaller.
What is the Regents Earth Science Moon Phases Worksheet?
The Regents Earth Science Moon Phases Worksheet helps students comprehend, visualize, and apply their knowledge of the Moon’s phases. Typically, the worksheet provides a series of activities that require students to:
- Determine and label the moon’s various phases.
- Explain the sequence of the phases
- Describe the positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon during each phase
- Relate the Moon’s phases to real-world phenomena, such as tides and eclipses
This worksheet is a valuable resource for both practicing and reinforcing your understanding of the Moon’s phases. It also helps prepare students for questions related to the Moon phases that often appear on the Regents Earth Science exam.
How to Use the Regents Earth Science Moon Phases Worksheet Effectively
To maximize your understanding of the Moon’s phases, it’s crucial to approach the worksheet step-by-step. Here’s how you can use the worksheet effectively:
Step 1: Familiarize Yourself with the Moon Phases
Before starting the worksheet, make sure you know the names of all eight phases. You can use diagrams or models of the Moon to help you visualize what each phase looks like. There are many helpful charts and animations online that illustrate the Moon’s phases. Understanding these basic concepts will make completing the worksheet much easier.
Step 2: Label the Phases
The Moon’s cycle is depicted in many worksheets, and you must accurately label each phase. Make sure you write the phase names in the correct sequence: Waxing Crescent, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, Waning Crescent, First Quarter, and Last Quarter.
Because it aids with sequence memorization, this stage is crucial. Using phrases like “the First Quarter occurs when half the Moon is visible” or “the Full Moon happens when the entire Moon is illuminated” can help link each phase to specific events or changes.
Step 3: Recognize the Sun, Earth, and Moon’s Positions
The position of the Sun, Earth, and Moon is critical in understanding why each phase occurs. The worksheet may ask you to describe these positions during each phase. For example:
- During the New Moon, the Moon is directly between the Earth and the Sun.
- The Earth is positioned between the Sun and the Moon during a full moon.
Understanding these positions helps you visualize how the phases change. You can draw diagrams to reinforce your understanding, which will also make it easier when you are required to answer questions on this topic in the future.
Step 4: Complete Practice Questions
After labeling the phases and understanding the positions, the worksheet will often include practice questions. They might ask you to describe the Moon’s phase after a certain amount of time or explain how the phases influence tidal patterns on Earth.
Answering these questions will test your comprehension of the material and prepare you for similar questions on the Regents exam. If you find yourself struggling with any question, review the material again, or ask your teacher for clarification.
Step 5: Make Connections with Other Concepts
While the Moon phases are a standalone topic, they also connect to other important Earth science concepts. For example, the phases of the Moon are closely linked to tides on Earth. The gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun affects the Earth’s oceans, causing high and low tides.
Additionally, lunar eclipses and solar eclipses are phenomena that occur due to the alignment of the Earth, Moon, and Sun. Understanding the Moon phases will help you grasp these phenomena better, making the Regents Earth Science exam questions easier to handle.
Key Topics to Review for the Regents Exam
While studying the Regents Earth Science Moon Phases Worksheet, keep these key topics in mind to ensure you’re fully prepared:
- Lunar Cycle and the Phases: Be able to define each phase and describe the position of the Sun, Earth, and Moon for each phase.
- Tides and the Moon: Understand the connection between the Moon’s phases and tidal patterns. The gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun causes the Earth’s oceans to experience high and low tides.
- Eclipses: Be familiar with lunar and solar eclipses. Know the conditions required for each type of eclipse and the positions of the Earth, Sun, and Moon that cause them.
- Synodic Month: The time it takes for the Moon to complete a full cycle of phases is called a synodic month, which lasts about 29.5 days. This concept is important to understand when answering questions about the Moon’s cycles.
- Moon’s Effect on Earth: Beyond tides, the Moon has an impact on Earth in other ways, including its influence on the planet’s rotation and axial tilt.
Tips for Acing the Regents Earth Science Exam
Here are a few final tips to ensure success when you face questions about the Moon’s phases in the Regents Earth Science exam:
- Practice with Diagrams: Drawing and labeling diagrams of the Moon’s phases is one of the best ways to prepare. The more practice you get, the better you will understand the cycle.
- Use Flashcards: Create flashcards with the names of the Moon phases on one side and their descriptions or positions on the other side. Flashcards are an excellent way to review material quickly.
- Review Past Exam Questions: Look at past Regents exams and practice questions related to the Moon phases. This will give you a feel for the kinds of questions that may be asked and help you prepare your answers more efficiently.
- Ask for Help: If you’re struggling with any concept related to Moon phases, don’t hesitate to ask your teacher or a tutor for help. Understanding the Moon’s phases will not only help you in the exam but will also make Earth science more enjoyable.
FAQ: Comprehending the Moon Phases Worksheet for Regents Earth Science
1. What are the main Moon phases I need to know for the Regents Earth Science exam?
The eight main Moon phases to know are: New Moon, Waxing Crescent, First Quarter, Waxing Gibbous, Full Moon, Waning Gibbous, Last Quarter, and Waning Crescent. These phases represent the changing appearance of the Moon as it orbits Earth.2. How does the Moon’s position affect its phases?
The Moon’s phases depend on its position relative to Earth and the Sun. The Moon is between Earth and the Sun when the New Moon occurs. During the Full Moon, Earth is between the Moon and the Sun, making the entire face of the Moon visible.3. What is the purpose of the Regents Earth Science Moon Phases Worksheet?
The worksheet helps students visualize and understand the sequence of the Moon’s phases. It includes activities like labeling diagrams, answering questions about the positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon, and connecting the phases to other phenomena like tides and eclipses.4. How do the Moon phases relate to tides on Earth?
The Moon’s phases influence the gravitational pull on Earth’s oceans, which causes high and low tides. During the Full and New Moon phases, when the Sun, Earth, and Moon align, tides are higher (spring tides). The tides are lower (neap tides) in the First and Last Quarters.5. How can I use the Moon Phases Worksheet to prepare for my Regents exam?
To prepare, practice labeling the Moon phases on diagrams, understand the positions of the Sun, Earth, and Moon during each phase, and answer practice questions. Use flashcards and review past exam questions to reinforce your knowledge and test your understanding.
Conclusion
The Regents Earth Science Moon Phases Worksheet is a valuable tool for mastering one of the most fundamental concepts in Earth science. By studying the sequence of the Moon’s phases, their causes, and their effects on Earth, you will prepare yourself well for the Regents exam. Keep practicing with worksheets, flashcards, and diagrams, and make sure to connect the Moon phases with related topics such as tides and eclipses. With these strategies in hand, you’ll be ready to ace the exam and deepen your appreciation for the dynamic relationship between the Earth and the Moon.
Blog
Paper Screening Based Test Ph-V for DM (B-15) Domicile holders of Nowshera, Charsadda & Malakand District in the E&SED Khyber Pakhtunkhwa [TEST DATE: 1st June’ 2025]
Candidate’s Answer Sheet Section
PST (BPS-12), CT (BPS-15), PET (BPS-15), DM (BPS-15), TT (BS-15)
Blog
How to gain High-Value clients on LinkedIn?

Key Points
- Research suggests optimizing your LinkedIn profile and engaging with your network can help gain a clients on LinkedIn.
- It seems likely that building relationships through personalized outreach and providing value are effective strategies.
- The evidence leans toward consistency and patience being crucial for success on LinkedIn.
Optimize Your Profile
Start by ensuring your LinkedIn profile is professional and appealing. Use a clear headshot, craft a headline that highlights what you offer, and write a summary showcasing your expertise. This makes you more visible to potential clients.
Build and Engage Your Network
Connect with industry professionals and potential clients, personalizing your requests to increase acceptance. Engage by liking, commenting, and sharing their posts, and join relevant LinkedIn groups to expand your reach.
Reach Out and Provide Value
Send personalized messages to potential clients, focusing on building relationships rather than selling immediately. Share useful content, offer free resources, or host webinars to demonstrate your expertise and build trust.
Move Conversations Offline and Be Consistent
Once you’ve built rapport, suggest a call or meeting to discuss how you can help. Stay consistent with daily engagement, as gaining clients on LinkedIn takes time and persistence.
Detailed Strategies for Gaining Clients on LinkedIn
This section provides a comprehensive guide based on extensive research into LinkedIn client acquisition strategies, drawing from multiple authoritative sources. The following details expand on the key points, offering a step-by-step approach for users looking to leverage LinkedIn effectively.
Profile Optimization: The Foundation for Visibility
Your LinkedIn profile is your digital storefront, and optimizing it is critical for attracting clients. Use a professional headshot to make a strong first impression, as profiles with photos receive more views. Craft a compelling headline that clearly states your value proposition, such as “Freelance Graphic Designer Helping Brands Stand Out” rather than a generic title like “Designer.” The summary should highlight your expertise, past achievements, and what you offer, using relevant keywords to improve search visibility. For example, if you’re targeting marketing agencies, include terms like “digital marketing,” “brand strategy,” and “client growth.”
Research from Dripify: How to Get Clients From LinkedIn emphasizes using SEO techniques, such as incorporating keywords in your headline and summary, to ensure your profile appears in searches. Additional resources, such as Dripify: Improve LinkedIn Profile and Dripify: LinkedIn SEO, provide detailed tips on enhancing visibility.
Identifying and Targeting Ideal Clients
To gain clients, you must first define your ideal customer avatar. This involves identifying their industry, job titles, and pain points. For instance, if you’re a web developer, target marketing managers in e-commerce firms. Use LinkedIn’s advanced search to filter by keywords, location, and industry, and consider Boolean operators (e.g., “web development” AND “e-commerce”) for refined results, as suggested by Dripify: Boolean Search on LinkedIn.
For advanced targeting, LinkedIn Sales Navigator offers features like lead recommendations and saved leads, though it’s a paid tool. The LinkedIn Sales Blog: 7 Steps to Attract More Clients With LinkedIn recommends using Sales Navigator for criteria like title and industry, with insights from LinkedIn: How to Use Sales Navigator.
Building and Engaging Your Network
Networking is at the heart of LinkedIn client acquisition. Start by connecting with colleagues, former clients, and industry leaders, personalizing each request to increase acceptance rates. For example, mention a shared interest or connection in your message. Engage with your network by liking, commenting, and sharing their posts, which helps build rapport.
Participating in LinkedIn groups is another effective strategy. Join groups relevant to your industry, such as “Digital Marketing Professionals,” and contribute by answering questions or sharing insights. Dripify: LinkedIn Groups highlights this as a way to connect with potential clients. Additionally, publishing thought leadership content, such as LinkedIn Articles addressing audience pain points, can position you as an expert. An example is the article “5 Game-Changing Digital Marketing Strategies for Small Businesses,” as noted in Dripify: LinkedIn Articles.
Personalized Outreach and Relationship Building
Once connected, avoid the mistake of immediate pitching, which can alienate potential clients. Instead, send personalized messages that focus on building relationships. For instance, ask about their current challenges or share a relevant article. The LinkedIn Sales Blog advises speaking like a human, finding commonalities, and following advice from experts like Will Allred on communication, available at LinkedIn: Don’t Pitch and Connect.
The DigitalMarketer: Build a Steady Stream of Clients suggests a non-salesy welcome message, including a question like “Tell me something interesting about your work,” to drive engagement. This approach, informed by Ted Prodromou’s book Ultimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business, emphasizes helping without expecting immediate returns, pretending you’re at a coffee meeting.
Providing Value to Build Trust
Providing value is crucial for converting connections into clients. Share resources, guides, or e-books that address your target audience’s pain points. For example, host a webinar on “Effective Social Media Strategies for Small Businesses” to showcase your expertise. Dripify: Create Value for Customers offers ideas like sharing case studies or hosting workshops.
Engaging in conversations is also key—be proactive by offering insights on posts or articles, and ask questions to spark dialogue. This builds trust and positions you as a helpful resource, as noted in Dripify: How to Get Clients From LinkedIn.
Moving Conversations Offline and Closing Deals
After building rapport, transition relationships offline by suggesting a phone call or virtual meeting. The DigitalMarketer process includes inviting responders to a short call, asking, “Would you like my help?” at the end, and closing deals via these interactions. The LinkedIn Sales Blog emphasizes demonstrating credibility before moving offline, ensuring you’ve established value.
Leveraging Recommendations and Referrals
Recommendations enhance your profile’s credibility, making it easier to attract clients. Ask satisfied clients or colleagues for recommendations, highlighting specific projects. For example, request, “Could you recommend me based on our recent website redesign project?” Follow up with gratitude, as outlined in Dripify: LinkedIn Recommendations, which lists five steps: identify connections, personalize, highlight relationships, be specific, and express gratitude.
Additionally, leverage your existing network for referrals. Reach out to former colleagues or friends, personalizing messages to seek introductions, as suggested in Dripify: How to Get Clients From LinkedIn.
Consistency and Patience: The Long-Term Approach
Gaining clients on LinkedIn requires consistency. Dedicate 30 minutes daily to engage, as per the DigitalMarketer 8-step process, which includes connecting, messaging, and following up. The LinkedIn Sales Blog stresses building your reputation over time, with success stories like Darren McKee, who gained 1,000 followers per week by posting consistently for over 1,000 days, detailed at LinkedIn: Posted on LinkedIn 950 Days Straight.
Patience is key, as results take time. The Dripify article notes LinkedIn’s 800 million members worldwide offer immense potential, but building relationships is a gradual process.
Additional Strategies for Advanced Users
For those looking to scale, consider using LinkedIn automation tools like Dripify for connection requests and follow-ups, ensuring compliance with LinkedIn’s policies, as detailed at Dripify: LinkedIn Automation Tools. Optimize your Social Selling Index (SSI) for better performance, with tips at Dripify: LinkedIn SSI Score. Drive traffic to your website via your profile link, share content, and use LinkedIn ads for broader reach, as noted in Dripify: Increase Website Traffic Using LinkedIn.
Collaborate with influencers for guest posts or joint webinars to expand your audience, as suggested at Dripify: Digital Marketing Experts. For hidden profiles, use LinkedIn X-Ray Search, detailed at Dripify: LinkedIn X-Ray Search.
Tables: Key Strategies and Tools
Below is a table summarizing the core strategies, with corresponding tools and resources:
| Strategy | Description | Tools/Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Profile Optimization | Enhance visibility with professional photo, headline, summary, keywords. | Dripify: Improve LinkedIn Profile, Dripify: LinkedIn SEO |
| Network Building | Connect with professionals, personalize requests, engage via likes/comments. | Dripify: Self-Entrepreneur LinkedIn |
| Group Engagement | Join industry groups, participate in discussions, share expertise. | Dripify: LinkedIn Groups |
| Content Publishing | Share articles addressing pain points, engage in comments. | Dripify: LinkedIn Articles |
| Advanced Search | Use keywords, filters, Boolean operators for targeted searches. | Dripify: Boolean Search on LinkedIn |
| Sales Navigator | Advanced filters, lead recommendations, InMail for direct messaging. | Dripify: How to Use LinkedIn Sales Navigator |
| Recommendations | Request from clients, highlight projects, express gratitude. | Dripify: LinkedIn Recommendations |
| Value Provision | Share resources, host webinars, address audience challenges. | Dripify: Create Value for Customers |
Another table for daily engagement, based on the 8-step process:
| Step | Daily Action | Time Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Identify ideal customer, use worksheet for targeting. | 5 minutes |
| 2 | Define problems you solve, focus on results. | 5 minutes |
| 3 | Optimize profile, ensure headline and summary attract clients. | 5 minutes |
| 4 | Connect, send non-salesy messages, include questions. | 5 minutes |
| 5 | Keep in touch, share relevant content every few months. | 5 minutes |
| 6 | Invite to calls, ask if they need help, close deals. | 5 minutes |
| 7 | Build authority, write recommendations, prompt reciprocation. | 5 minutes |
| 8 | Repeat steps 4-7 daily, maintain consistency. | Ongoing |
Success Stories and Statistics
Success stories underscore the potential of these strategies. Darren McKee’s consistent posting for over 1,000 days resulted in 1,000 followers per week, as detailed at LinkedIn: Posted on LinkedIn 950 Days Straight. The DigitalMarketer process helped create a six-figure business, with Ted Prodromou’s book Ultimate Guide to LinkedIn for Business providing further insights. LinkedIn’s 800 million members, as noted in Dripify, offer a vast pool for client acquisition.
Conclusion
Gaining clients on LinkedIn is a multifaceted process requiring profile optimization, targeted networking, engagement, and consistent effort. By following these strategies, users can build relationships, provide value, and ultimately secure clients, with patience being essential for long-term success.
Blog
How to Make Vegan Leather from Recycled Materials: A Step-by-Step Guide

In recent years, vegan leather has become a cruelty-free and eco-friendly alternative to traditional animal leather. But did you know you can take sustainability a step further by creating vegan leather from recycled materials? This innovative approach reduces waste, lowers carbon footprints, and empowers you to craft stylish, durable goods at home.
This guide explores simple, creative methods to make vegan leather using everyday recycled items like plastic bottles, cork, pineapple leaves, and more. Let’s dive in!
Why Choose Vegan Leather from Recycled Materials?
Traditional leather production harms the environment through deforestation, water pollution, and methane emissions from livestock. Vegan leather offers a compassionate alternative, but many store-bought options rely on synthetic plastics like PVC, which aren’t biodegradable.
By using recycled materials, you:
- Reduce landfill waste (e.g., repurposing plastic bottles or fruit scraps).
- Save resources (no need for virgin plastics or animal farming).
- Create customizable, unique textures (each material has its look and feel!).
Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a sustainability advocate, making vegan leather at home is a fun, impactful project.
Materials You Can Use to Make Vegan Leather
Almost any flexible, durable recycled material can become vegan leather! Here are the most popular options:
- Recycled Plastic (rPET): Plastic bottles, packaging, or old polyester fabrics.
- Cork: Wine corks, corkboard scraps, or industrial cork waste.
- Plant-Based Fibers: Pineapple leaves (Piñatex), apple peels, or mushroom mycelium.
- Upcycled Fabrics: Denim, canvas, or rubber from old tires.
Each material requires slightly different techniques. Below, we’ll break down five easy methods.
Method 1: Recycled Plastic Bottle Leather (rPET)
Materials Needed:
- Clean plastic bottles (PET)
- Scissors or craft knife
- Non-toxic adhesive (e.g., cornstarch glue)
- Baking parchment
- Iron or heat press
Steps:
- Prepare the Plastic:
Cut bottles into flat sheets. Remove labels and caps, then slice vertically. Flatten the pieces and trim the edges. - Create Layers:
Overlap plastic pieces on baking parchment. Apply adhesive between layers to bond them. - Press and Heat:
Cover with another parchment sheet. Iron at medium heat (150°C/300°F) for 10–15 seconds, applying even pressure. Repeat until layers fuse into a flexible sheet. - Finish:
Let cool. Sand edges for smoothness, or dye with natural pigments for color.
Best For: Bags, wallets, and accessories. rPET leather is water-resistant and sturdy!
Method 2: Cork Leather from Wine Corks
Materials Needed:
- Wine corks (10–15 for a small sheet)
- Food processor or grater
- Non-toxic binder (flour paste or eco-friendly glue)
- Rolling pin
- Wax paper
Steps:
- Shred the Corks:
Grate corks into fine granules using a food processor. Avoid plastic-backed corks. - Mix with Binder:
Combine cork granules with binder until it forms a dough-like consistency. - Roll and Dry:
Place the mixture between wax paper sheets. Roll flat (3–5mm thick). Air-dry for 24–48 hours. - Seal (Optional):
Brush with beeswax or linseed oil for a polished, water-resistant finish.
Best For: Notebook covers, coasters, or jewelry. Cork is lightweight and naturally textured.
Method 3: Pineapple Leaf Leather (Piñatex)
Materials Needed:
- Pineapple leaves (from 5–6 pineapples)
- Blender
- Natural dye (optional)
- Cornstarch or agar-agar (as a binder)
- Mesh screen or cloth
Steps:
- Extract Fibers:
Boil leaves for 30 minutes to soften. Scrape off pulp with a knife, revealing long fibers. Rinse and dry. - Blend and Bind:
Mix fibers with 1 cup water and 2 tbsp binder in a blender. Pour onto a mesh screen to form a thin layer. - Dry and Press:
Sun-dry for 2–3 days, pressing occasionally with a heavy book to flatten.
Best For: Shoes, belts, or upholstery. Piñatex has a rustic, fibrous appearance.
Method 4: Mushroom Leather (Mycelium)
Materials Needed:
- Mushroom mycelium starter kit (available online)
- Organic substrate (sawdust or straw)
- Baking tray
- Dehydrator or oven
Steps:
- Grow Mycelium:
Spread the substrate in a tray. Inoculate with mycelium spores. Store in a dark, humid place for 2–3 weeks. - Harvest and Press:
Once fully grown, peel the mycelium mat from the substrate. Press between boards to flatten. - Tan and Dry:
Soak in a natural tannin (like oak gall solution) for 1 hour. Dehydrate at 40°C (104°F) until leathery.
Best For: High-fashion items. Mycelium leather is biodegradable and mimics animal leather’s softness.
Method 5: Apple Peel Leather
Materials Needed:
- Apple peels (from 10–12 apples)
- Blender
- Glycerin or vegetable glycerin
- Baking sheet
Steps:
- Blend Peels:
Puree peels with 1 tbsp glycerin until smooth. - Spread and Dry:
Pour the mixture onto a baking sheet lined with parchment. Dry in sunlight or an oven at 50°C (120°F) for 8–12 hours. - Finish:
Peel off the sheet. Condition with coconut oil for flexibility.
Best For: Small accessories or decorative patches. Apple leather has a fruity scent and matte finish.
Customizing Your Vegan Leather
Make your creations stand out with these tips:
- Dyeing: Use turmeric (yellow), beet juice (pink), or spirulina (green).
- Embossing: Press leaves or lace into the material before drying.
- Stitching: Reinforce edges with upcycled thread or hemp cord.
Caring for Vegan Leather
- Cleaning: Wipe with a damp cloth. Avoid harsh chemicals.
- Storage: Keep in a cool, dry place to prevent mold.
- Repair: Patch tears with adhesive or a matching material piece.
Environmental Impact and Challenges
Pros:
- Reduces plastic and organic waste.
- Uses less water and energy than animal leather.
Cons:
- Some methods require practice to perfect.
- Plant-based leathers may be less durable than synthetics.
5 FAQs about How to Make Vegan Leather from Recycled Materials
1. Can I make vegan leather at home without specialized equipment?
Answer: Absolutely! Many methods for making vegan leather from recycled materials require only basic household items like scissors, a blender, an iron, or a baking sheet. For example, creating cork leather or apple peel leather can be done with minimal tools. While some techniques, like growing mushroom leather, may need a starter kit, most DIY vegan leather projects are beginner-friendly and don’t require expensive equipment.
2. How durable is vegan leather made from recycled materials compared to traditional leather?
Answer: The durability of vegan leather depends on the materials and methods used. For instance, recycled plastic bottle leather (rPET) is highly durable and water-resistant, making it ideal for bags and accessories. On the other hand, plant-based options like pineapple or apple leather may be softer and better suited for lightweight items. While vegan leather may not always match the longevity of traditional leather, proper care (like sealing and conditioning) can significantly extend its lifespan.
3. Is vegan leather from recycled materials biodegradable?
Answer: It depends on the materials used. Plant-based vegan leathers, such as those made from pineapple leaves, cork, or mushroom mycelium, are biodegradable and compostable. However, vegan leather made from recycled plastics (like rPET) is not biodegradable, though it still helps reduce waste by repurposing existing materials. If biodegradability is a priority, opt for natural, plant-based options.
4. Can I scale up DIY vegan leather production for small businesses?
Answer: Yes, you can! Many of the methods described in the article, such as using pineapple leaves or recycled plastics, can be scaled up with some adjustments. For example, investing in a heat press for rPET leather or a dehydrator for mushroom leather can streamline production. Additionally, sourcing bulk recycled materials and experimenting with efficient techniques can help you create consistent, high-quality vegan leather for a small business.
5. What are the best ways to dye vegan leather naturally?
Answer: Natural dyes are a great eco-friendly option for coloring vegan leather. You can use ingredients like turmeric (for yellow), beet juice (for pink), spirulina (for green), or coffee grounds (for brown). Simply mix the dye with water, apply it to the material using a brush or sponge, and let it dry. For a more vibrant color, repeat the process or add a natural fixative like vinegar. This approach is safe, sustainable, and adds a unique touch to your creations.
Final Thoughts
Creating vegan leather from recycled materials is a rewarding way to support sustainable fashion. Whether you’re crafting a wallet from plastic bottles or a chic bag from pineapple leaves, each project makes a difference. Ready to start? Gather your materials, experiment with textures, and share your creations to inspire others!
By embracing DIY vegan leather, you’re not just making accessories—you’re shaping a greener future.
Most People ask questions on Google about How to Make Vegan Leather from Recycled Materials
What is the process of making vegan leather?
Vegan leather is made without animal hides and instead uses plant-based or synthetic materials. The process varies depending on the type of material used but generally follows these steps:
- Material Sourcing – Vegan leather can be made from plants like mushrooms, pineapples, apples, cacti, or synthetic materials like polyurethane (PU).
- Processing & Treatment – Plant fibers are extracted and mixed with binders or resins to create a durable, leather-like texture. In synthetic versions, plastic is melted and spread into thin layers.
- Shaping & Drying – The material is shaped into sheets and left to dry. This stage determines its thickness and flexibility.
- Texturizing & Coloring – To mimic real leather, the material is embossed with a grain pattern and dyed using eco-friendly or synthetic dyes.
- Finishing Touches – A protective coating is applied for durability, water resistance, and longevity.
How do you make vegan plant-based leather?
Plant-based vegan leather is made using natural materials and fewer chemicals compared to synthetic alternatives. The process depends on the plant source but generally includes:
- Collection & Processing – Fruit waste (pineapple leaves, apple peels, etc.), cactus, or mushrooms are harvested and dried.
- Fiber Extraction & Blending – The plant fibers are broken down and mixed with natural binders like starch or plant-based resins to form a leather-like sheet.
- Shaping & Texturing – The material is rolled out, textured, and sometimes reinforced with fabric backings for extra strength.
- Tanning & Dyeing – The sheets are treated with natural tannins (from tree bark, for example) and dyed with plant-based or non-toxic dyes.
- Finishing – A protective, biodegradable coating is applied for durability and water resistance.
Popular plant-based vegan leathers include Piñatex (pineapple leather), Mylo (mushroom leather), and Desserto (cactus leather).
How do you recycle vegan leather?
Recycling vegan leather depends on its materials:
- Plant-based vegan leather is biodegradable, meaning it will naturally break down over time. Some types can be composted in industrial facilities.
- Synthetic vegan leather (PU, PVC) is harder to recycle due to plastic content. Some brands have take-back programs for recycling.
- Upcycling is another option—old vegan leather items can be repurposed into new accessories like wallets or keychains.
To be more eco-friendly, look for plant-based or recycled-material vegan leathers rather than plastic-based options.
What materials are used to make vegan leather?
Vegan leather is made from a variety of natural and synthetic materials, including:
🌱 Plant-Based Materials:
- Pineapple leaves (Piñatex)
- Cactus (Desserto)
- Mushrooms (Mylo)
- Apple peels
- Cork
- Banana fibers
🛠 Synthetic Materials:
- Polyurethane (PU)
- Recycled plastics (from bottles or industrial waste)
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) – less eco-friendly
The best vegan leathers are plant-based or made from recycled materials, as they are more sustainable than plastic-based versions.
What are the ingredients in vegan leather?
The ingredients vary depending on the type of vegan leather:
- Plant-Based Leather – Natural plant fibers, bio-based binders (like corn starch or natural resins), plant-based dyes, and protective coatings made from waxes or oils.
- Synthetic Vegan Leather – Polyurethane (PU) or PVC, plasticizers, synthetic dyes, and chemical coatings for texture and durability.
For an eco-friendly choice, look for low-plastic, biodegradable vegan leathers made from plants or recycled materials.
-

 Travel6 months ago
Travel6 months agoTop 5 Ways Stephen Revetria Elevates the U.S. Travel and Tourism Advisory Board
-

 Crypto7 months ago
Crypto7 months agoUnlock 7 Powerful Cryptocurrency Insights: Delving into NewzNav.com’s Crypto Archives
-

 Technology7 months ago
Technology7 months agoHydrogen Water Machines: Revolutionizing Hydration and Wellness
-
 NEWS & Society7 months ago
NEWS & Society7 months agoChurch of the Holy Spirit News: Events & Impact
-

 Games7 months ago
Games7 months agoDownload Tekken 6 PC: A Comprehensive Resource
